SAFERS
Structured Approaches for Forest fire Emergencies in Resilient Societies

The SAFERS project aims to develop a comprehensive, emergency management system for the management of forest fires. The project is funded by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under Grant Agreement No. 869353.
Abstract
Changing climate is increasing the risk of wildfires. As temperatures continue to soar in the future, scientists warn that extreme fires will become more common. Meaningful early warning forecasts, early identification and tracking as well as effective response are of paramount importance to save lives and contain environmental damage. The EU-funded SAFERS project will develop a complex emergency management system capable of acting along the whole emergency management cycle, thanks to the coupled use of heterogeneous Big Data, advanced models, and AI. Earth Observation data from Copernicus and GEOSS will be the primary data source, which will be combined with data from social media, smoke detectors, and mobile applications. This will allow first responders, citizens and decision makers to generate new and more accurate information, enhancing our society’s resilience against wildfires.
SAFERS Architecture
In the SAFERS platform, the architectural design, shown in the figure below, plays a crucial role in facilitating efficient communication, data management, and visualization of heterogeneous information. This section presents an overview of the architectural definition, highlighting the key modules that contribute to the platform’s functionality.
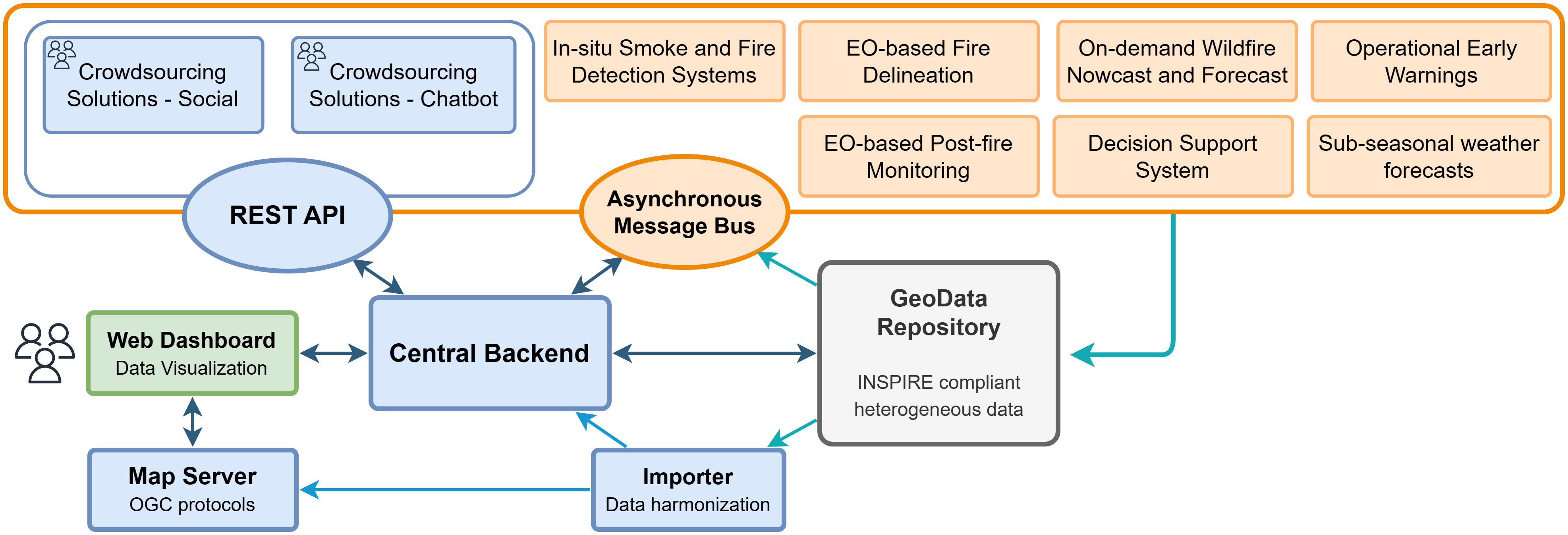
The main functionalities of the SAFERS platform are provided by the set of Intelligent Services (IS), independent of one another, and playing a vital role in providing valuable information and functionalities. The IS are grouped into three main categories, namely operational services, on-demand services, and crowdsourcing solutions. The operational services represent the modules with a simpler communication paradigm, autonomously providing periodical updates for specific data. These include Sub-seasonal Weather Forecasts, Operational Early Warnings, In-situ Smoke and Fire Detection Systems, and the Decision Support System.
On-demand services, namely the EO-based fire delineation, Post-fire Monitoring and On-demand Wildfire Forecast services, support instead a more complex communication mechanism, triggered by a specific message type named map request. As the name suggests, these services act on demand, retrieving the necessary data based on user-defined parameters, and produce one or more outputs, depending on the request. Once the results become available, the other services are notified through the message bus, allowing for the required follow-up actions to take place.
Last, SAFERS also incorporates crowdsourcing solutions, including a chatbot and a social media module, to gather information directly or indirectly from citizens. The chatbot enables structured geolocated and multimedia data collection, while the social module gathers and classifies real-time Twitter posts, extracting relevant emergency events and estimating their impacts.
To support efficient data management, the platform includes a data layer, which serves as a central storage system for heterogeneous data. This module adheres to INSPIRE standards, ensuring proper organization and accessibility of diverse datasets. When applicable, the raw data stored in the GeoData Repository (GDR) is processed by the Importer and Mapper modules. These components facilitate the management of OGC-compliant layers, enabling the integration and presentation of spatial data within the system, generating Web Map Tile Service (WMTS) layers on the tile server.
The main communication point between users and services is the central backend, which serves as the communication hub between users and services. It facilitates the exchange of information, allowing users to interact with various components of the platform seamlessly. This backend ensures the smooth flow of data and requests throughout the system. A web-based dashboard is provided to users for intuitive data visualization. The dashboard supports the display of geospatial information through Web Map Service (WMS) and Web Map Tile Service (WMTS) layers. Additionally, it incorporates social media data and real-time information from in-situ cameras, enabling users to gain valuable insights and make informed decisions.
Open Source Resources
Here you can find a collection of open source repositories that are part of the SAFERS project. The following core services are openly available on GitHub:
- SAFERS Dashboard Frontend
- SAFERS Dashboard Backend
- SAFERS GeoData Repository
- SAFERS Importer & Mapper
- SAFERS Message Broker
Technical Documentation
The technical documentation of the SAFERS platform is available at the following links:
Project Information
For further information or commercial support, please contact us at contact@safers-project.eu.